Vim Notes — Modal Text Editing and Efficient Navigation
Practical insights on modal editing, navigation techniques, and text manipulation workflows

Master the World’s Most Powerful Text Editor — From Beginner to Expert
Introduction to Vim
Why Learn Vim?
Vim is not just a text editor—it’s a philosophy of efficient editing. Once you understand Vim’s core concepts, you can edit text 5-10x faster than traditional editors. Used by developers, system administrators, and DevOps professionals worldwide.
Vim is a highly configurable modal text editor built on top of Vi (Unix’s classic text editor from 1976). It’s lightweight, powerful, and available on virtually every Unix-like system, making it the de facto standard for command-line editing.
Key Statistics:
- Age: First released in 1991 (34 years of continuous development)
- Popularity: Used by millions of developers and system administrators
- Learning Curve: Steep initially, exponential productivity gains
- Extensibility: Fully programmable via Vimscript or Lua
- Community: Massive ecosystem with thousands of plugins
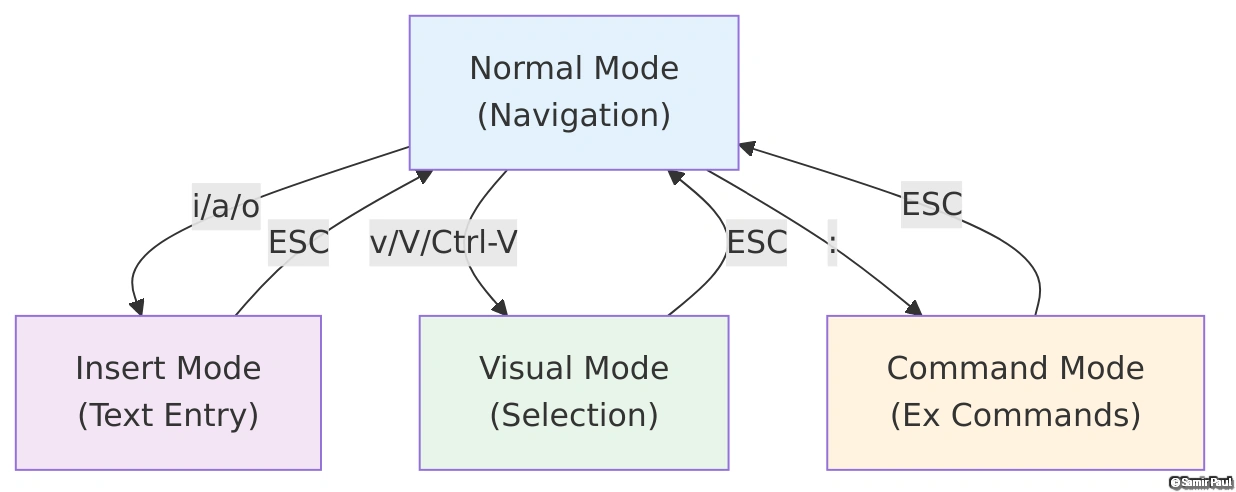
The Vim Philosophy: Modal Editing
Modal Editing Paradigm
Most editors use a single mode where keys always insert text. Vim separates concerns into distinct modes:
- Normal Mode: Navigation and commands (your home base)
- Insert Mode: Text insertion (like traditional editors)
- Visual Mode: Text selection and manipulation
- Command Mode: Advanced operations and configuration
This separation creates logical separation of concerns, making complex text operations intuitive once you understand the grammar.
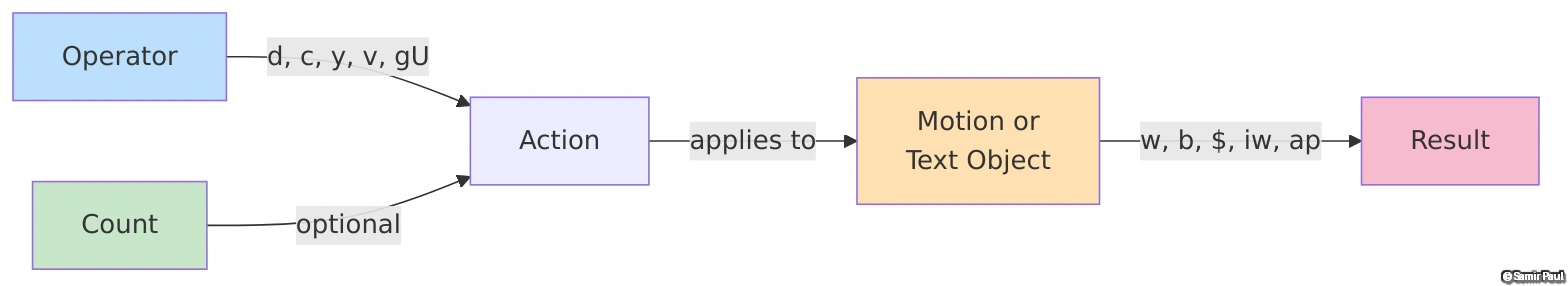
The Vim Grammar: Operator + Motion
Vim’s Killer Feature: Text Objects + Motions = Composable Editing
Vim operates on a grammar: operator + motion + (optionally) text-object
Examples:
dw= Delete word (delete + word motion)c5j= Change 5 lines down (change + 5-line motion)dip= Delete paragraph (delete + paragraph text object)
This composability means once you learn operators and motions, you can combine them infinitely!
Installation and Setup
Installing Vim
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update && sudo apt install vim
# CentOS/RHEL/Fedora (7)
sudo yum install vim
# CentOS/RHEL/Fedora (8+)
sudo dnf install vim
# macOS
brew install vim
# Or for newer Neovim (modern alternative)
brew install neovim
# Windows (using Chocolatey)
choco install vim
# Or download from https://www.vim.org/download.phpVerify Installation
# Check version and features
vim --version
# Output should show: VIM - Vi IMproved and version number
# Look for these important features (+):
# +python, +python3 (for plugins)
# +clientserver (for remote editing)
# +clipboard (for system clipboard)Initial Configuration
Create a basic .vimrc file in your home directory:
" Basic Vim Configuration
" This is your Vim initialization file
" Enable syntax highlighting
syntax on
" Use 24-bit colors
set termguicolors
" Line numbering
set number
set relativenumber
" Indentation
set tabstop=4 " Tab width
set shiftwidth=4 " Indent width
set expandtab " Use spaces instead of tabs
set autoindent " Auto-indent new lines
" Search behavior
set ignorecase " Ignore case in searches
set smartcase " But match case if uppercase is used
set incsearch " Highlight search as you type
" UI Enhancements
set statusline=%F%m%r%h%w\ [%{&ff}]\ %y\ [%p%%]\ %l:%c
set laststatus=2 " Always show status bar
set cursorline " Highlight current line
set showmatch " Highlight matching brackets
" Performance
set nocompatible " Use Vim defaults, not Vi
set lazyredraw " Don't redraw during macrosUnderstanding Vim Modes
Mode Transitions
Vim operates in distinct modes, each optimized for different tasks. Understanding how to transition between modes is essential:

1. Normal Mode (Command Mode)
Default mode for navigation and commands.
" Navigation
h, j, k, l = Left, Down, Up, Right (arrow keys equivalent)
w, W = Next word, next WORD
b, B = Previous word, previous WORD
0, $ = Start of line, end of line
gg, G = Start of file, end of file
{, } = Previous/next paragraph
" Editing
x, X = Delete character under/before cursor
dd = Delete entire line
yy = Yank (copy) entire line
p, P = Paste after/before cursor
u = Undo
CTRL-R = Redo
" Operators
d = Delete
c = Change (delete and enter insert mode)
y = Yank (copy)2. Insert Mode
For typing text. Behaves like traditional editors.
i = Insert at cursor position
I = Insert at line beginning
a = Append after cursor
A = Append at line end
o = Open new line below
O = Open new line above
s = Substitute character (delete char, enter insert mode)
S = Substitute entire line
" While in Insert Mode, press ESC to return to Normal Mode
" Or use CTRL-C as an alternative3. Visual Mode
Select text for operations.
v = Character-wise visual mode (select characters)
V = Line-wise visual mode (select entire lines)
CTRL-V = Block visual mode (select rectangular block)
" In visual mode:
d = Delete selection
y = Yank selection
c = Change selection
u = Convert to lowercase
U = Convert to uppercase4. Command Mode (Ex Commands)
Execute commands using the colon (:) prefix.
:w = Save file
:q = Quit
:wq = Save and quit
:e filename = Open file
:set option=val = Set configuration
:%s/old/new/g = Replace all occurrences
:10,20d = Delete lines 10-20Essential Motions and Movements
Master These Motions First
Motions are the “nouns” in Vim’s grammar. Combine them with operators to create powerful commands. These are your most-used building blocks.
Character-Level Motions
h = One character left
l = One character right
j = One line down
k = One line up
fx = Find character 'x' on this line (forward)
Fx = Find character 'x' on this line (backward)
tx = Until character 'x' (forward, stops before)
Tx = Until character 'x' (backward, stops before)
; = Repeat last f/F/t/T motion
, = Repeat last f/F/t/T motion backwards
% = Jump to matching bracket/parenthesisWord Motions
w = Next word (beginning of next word)
W = Next WORD (separated by whitespace only)
e = End of current word
E = End of current WORD
b = Beginning of previous word
B = Beginning of previous WORD
" Difference between word and WORD:
" word splits on whitespace and punctuation
" WORD splits on whitespace only
Example: foo-bar-baz
word motions: foo | -bar | -baz
WORD motions: foo-bar-baz (entire thing is one WORD)Line Motions
0 = Start of line
^ = First non-whitespace character
$ = End of line
g_ = Last non-whitespace character
_ = Absolute beginning of line (vim-specific)Paragraph and Block Motions
{ = Previous paragraph
} = Next paragraph
( = Previous sentence
) = Next sentence
[{ = Previous opening brace
]} = Next closing braceFile Motions
gg = Beginning of file
G = End of file
:50<Enter> = Go to line 50
50G = Go to line 50 (from normal mode)
CTRL-G = Show current position in file
<number>% = Go to percentage of file (50% = halfway)Core Operators
Essential Operators
d (delete) Delete motion and remove from buffer
c (change) Delete motion and enter insert mode
y (yank) Copy motion to register
v (visual) Select motion character-wise
V (visual) Select motion line-wiseOperator Examples
dw = Delete from cursor to end of word
d5w = Delete 5 words
dd = Delete entire line
d$ = Delete from cursor to end of line
dip = Delete entire paragraph
cw = Change word (delete word, enter insert mode)
C = Change to end of line (shortcut for c$)
cc = Change entire line (shortcut for S)
yy = Copy entire line
y$ = Copy from cursor to end of line
ynw = Copy next wordText Objects: The Power Multiplier
Text Objects are Game Changers
Text objects let you operate on semantic units (words, sentences, paragraphs, quotes, brackets) rather than just character counts. This is what makes Vim editing feel “smart.”
Text Object Syntax
operator + a/i + object
↑ ↑
Action Type
a = around (include delimiters)
i = inner (exclude delimiters)Common Text Objects
" Word objects
iw = inner word (just the word)
aw = a word (word + surrounding whitespace)
" WORD objects
iW = inner WORD
aW = a WORD
" Paragraph
ip = inner paragraph
ap = a paragraph
" Quoted strings
i', i", i` = inside single, double, backticks
a', a", a` = around quotes
" Brackets and parentheses
i(, i), ib = inside parentheses
a(, a), ab = around parentheses
i{, i}, iB = inside braces
a{, a}, aB = around braces
i[, i] = inside brackets
a[, a] = around brackets
i<, i> = inside angle brackets
a<, a> = around angle brackets
" Tags (for HTML/XML)
it = inner tag
at = a tagReal-World Text Object Examples
diw = Delete inside word (replace word easily)
ci" = Change inside quotes (edit string content)
da{ = Delete around braces (remove function body)
vip = Select inside paragraph (visual select)
yip = Copy paragraph
gUi( = Uppercase inside parentheses
" Example: Change function argument
function(arg1, [cursor here], arg3)
ci( → change inside parentheses
→ Now type new content, replaces (arg1, arg2, arg3)Search and Replace
Search Operations
/pattern = Search forward for pattern
?pattern = Search backward for pattern
n = Next match (forward)
N = Previous match (backward)
* = Search for word under cursor (forward)
# = Search for word under cursor (backward)
" Repeat last search
; (in f/F/t/T) = Repeat last find
/ then Enter = Repeat last search patternSearch Configuration
set ignorecase = Ignore case when searching
set smartcase = Override ignorecase if uppercase present
set incsearch = Show matches as you type
set hlsearch = Highlight all matches
:nohlsearch = Clear highlighting (also :noh)Find and Replace (Substitute)
" Basic syntax: :[range]s/pattern/replacement/[flags]
:s/old/new/ = Replace first occurrence on current line
:s/old/new/g = Replace all occurrences on current line
:%s/old/new/g = Replace all in entire file
:%s/old/new/gc = Replace all with confirmation
:5,10s/old/new/ = Replace on lines 5-10
" Common flags:
g = Global (replace all on line, not just first)
c = Confirm before each replacement
i = Ignore case
e = Don't show error if pattern not found
" Special characters in replacement:
& = Full match of pattern
\1, \2, etc. = Captured groups (if using regex)
~ = Previous replacement stringRegular Expressions
" Basic patterns
. = Any character
* = Zero or more of previous
\+ = One or more of previous
\? = Zero or one of previous
^ = Start of line
$ = End of line
\s = Whitespace
\w = Word character
\d = Digit
" Examples:
:%s/\d\+/NUM/g = Replace all numbers with "NUM"
:%s/\s+$// = Remove trailing whitespace
:%s/^ // = Remove leading spaces
:%s/foo\(.*\)bar/\1/ = Extract middle part
" Special: Use \< and \> for word boundaries
:%s/\<old\>/new/g = Replace whole word "old" onlyRegisters: Vim's Advanced Clipboard
Registers are Vim’s Clipboard on Steroids
While most editors have one clipboard, Vim has 26+ registers! This lets you copy multiple things and paste any of them. Essential for advanced editing.
Register Types
" Named registers (a-z)
"a = Register a
"b = Register b
(... up to "z)
" Special registers
"0 = Last yank (copy)
"1 to "9 = Last 9 deletions
""- = Last small deletion
""/ = Last search pattern
": = Last command
"% = Current filename
"# = Alternate filename
"+ = System clipboard
"* = Selection clipboard (X11)
"= = Expression register
". = Last inserted textUsing Registers
" Copying to registers
"ayy = Yank line into register a
"a5yy = Yank 5 lines into register a
"ad5w = Delete 5 words into register a
" Pasting from registers
"ap = Paste register a
"bp = Paste register b
"=5+3<Enter>p = Paste result of expression (8)
" Inserting in Insert Mode
<CTRL-R>a = Insert contents of register a while in insert mode
<CTRL-R>=3*4<Enter> = Insert result of expression (12)
" Appending to registers (uppercase = append)
"Ayy = Append current line to register a
"Ad5w = Append 5 words to register aPractical Register Workflows
" Copy email for later use
0
"ey$ = Copy email (from start of line to end) to register e
" Create template by copying structure
"tyy = Copy template line to register t
3j = Move 3 lines down
"tp = Paste template 3 times
" System clipboard (most useful!)
"+yy = Copy line to system clipboard
"+p = Paste from system clipboardMacros: Automating Complex Tasks
Macros Let You Record and Replay Editing Sequences
Record a series of keystrokes and replay them. Perfect for repetitive tasks like formatting, bulk editing, or complex multi-step operations.
Recording Macros
" Recording
q + register = Start recording to register (q for quit recording)
qa = Start recording to register 'a'
... (type edits)
q = Stop recording (press q again)
" Playing
@a = Play macro from register 'a'
3@a = Play macro 3 times
@@ = Play last macro (convenient repeat)
" Editing macros
"ap = Paste macro into buffer (to view it)
... (edit)
"ay$ = Copy edited version back to register
" Example: Record complex edit
qa = Start recording
I = Insert at beginning
// TODO:
<ESC> = Back to normal mode
A (at end) = Append at end
= Start recording again
q = Stop recording
Now "@a" will add "// TODO:" comments!Advanced Macro Techniques
" Macro on range (execute on lines 1-10)
:1,10 normal @a
" Macro on all lines matching pattern
:g/pattern/ normal @a
" Conditional macro execution
:if condition
: normal @a
:endif
" Chain macros (macro calls another macro)
qa = Start recording
@b = Call macro b
@c = Call macro c
q = Stop recordingReal-World Macro Example
" Original data:
name:John,age:30,city:NYC
" Goal: Convert to JSON format
{"name":"John","age":30,"city":"NYC"}
" Macro steps:
qa = Start recording in register a
^ = Go to start of line
i{ = Insert {
<ESC> = Return to normal mode
:s/:/ /g = Replace colons with spaces
:s/,/", "/g = Replace commas with quotes
... more edits
$ = Go to end
a} = Append }
<ESC> = Done
q = Stop recording
@a = Execute macroVisual Mode and Selection
Visual Mode Types
v = Character-wise visual mode
Select individual characters
V = Line-wise visual mode
Select entire lines (most intuitive)
CTRL-V = Block visual mode
Select rectangular blocks (powerful!)Visual Mode Operations
" Selection in visual mode
v / V / CTRL-V = Activate mode
h,j,k,l = Expand/contract selection
w,b,e = Move by words
$, ^, 0 = Move by line
G, gg = Move by file
" Operators on selection
d, x = Delete selection
c = Change selection
y = Yank selection
> = Indent right
< = Indent left
u = Lowercase
U = Uppercase
= = Auto-indentBlock Visual Mode Examples
" Add comment prefix to multiple lines
CTRL-V = Start block select
3j = Select 3 lines down
$ = Select to end of lines
= Now have rectangular selection
I// <ESC> = Insert "// " at beginning of each line
" Insert column of text
CTRL-V = Start block mode
3j = Select 4 lines
$ = Select to end
A:<ESC> = Append ":" to end of each line
" Replace in column
CTRL-V = Select rectangle
c = Change
new_text = Type replacement
<ESC> = Applied to all lines in selectionMarks and Jumps: Navigate Like a Pro
Marks: Bookmarks for Your Code
Marks let you set bookmarks in files and jump between them instantly. Essential for navigating large codebases or editing multiple sections.
Setting and Using Marks
" Setting marks
ma = Set mark 'a' at current position
mB = Set mark 'B' at current position
m[a-z] = Local marks (per-buffer)
m[A-Z] = Global marks (across files)
" Jumping to marks
`a = Jump to exact position of mark 'a' (line + column)
'a = Jump to line of mark 'a' (column 0)
`A = Jump to global mark A (even across files!)
" Special marks (automatic)
`` = Position before last jump
`. = Last change position
`" = Position when last exited file
`[ = Start of last changed or yanked text
`] = End of last changed or yanked text
`< = Start of last visual selection
`> = End of last visual selection
" List all marks
:marks = Show all active marks
:delmarks a = Delete mark 'a'
:delmarks! = Delete all lowercase marksJump List Navigation
CTRL-O = Jump to older position (jump back)
CTRL-I = Jump to newer position (jump forward)
:jumps = Show jump list history
" Change list
g; = Go to older change position
g, = Go to newer change position
:changes = Show change list
" Practical workflow
1. Browse code with searches and motions
2. CTRL-O to jump back through history
3. CTRL-I to jump forwardMarks Workflow Diagram
Visualizing how marks work across files helps understand their power for navigation:
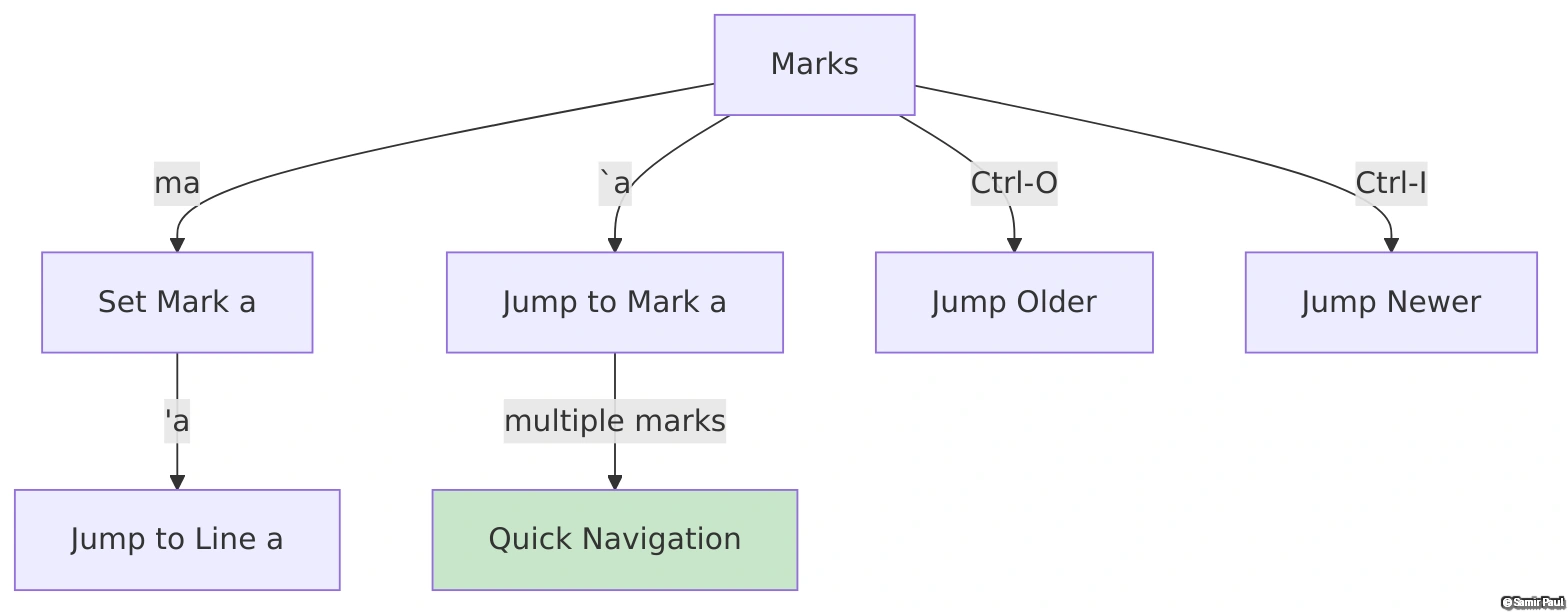
Remember: Local marks (a-z) are file-specific, while global marks (A-Z) work across files!
Code Folding: Manage Large Files
Folding Collapses Code Sections
Like collapsing functions in an IDE. Essential for navigating large files by hiding sections you’re not currently editing.
Folding Commands
" Manual folding
zf{motion} = Create fold (e.g., zf5j = fold next 5 lines)
zf% = Fold matching bracket pair
{Visual}zf = Create fold from visual selection
" Opening/closing folds
zo = Open fold under cursor
zc = Close fold under cursor
za = Toggle fold (open if closed, close if open)
zO = Open all folds recursively under cursor
zC = Close all folds recursively under cursor
" All folds in buffer
zM = Close ALL folds in buffer
zR = Open ALL folds in buffer
zm = Fold more (close one level)
zr = Fold less (open one level)
" Navigating folds
zj = Move to next fold
zk = Move to previous fold
[z = Move to start of current open fold
]z = Move to end of current open fold
" Delete folds
zd = Delete fold under cursor
zD = Delete all folds under cursor recursively
zE = Eliminate all folds in bufferFolding Methods
" Choose folding method
set foldmethod=manual " Manual folding (default)
set foldmethod=indent " Fold by indentation level
set foldmethod=syntax " Fold based on syntax (for code)
set foldmethod=expr " Fold using custom expression
set foldmethod=marker " Fold using {{{ }}} markers
" Fold configuration
set foldlevel=0 " Close all folds by default
set foldlevelstart=99 " Start with all folds open
set foldnestmax=3 " Maximum fold nesting
" Example: Python folding by indent
autocmd FileType python setlocal foldmethod=indent foldlevel=0Folding Visualization
See how folding transforms a 100-line file into a manageable overview:
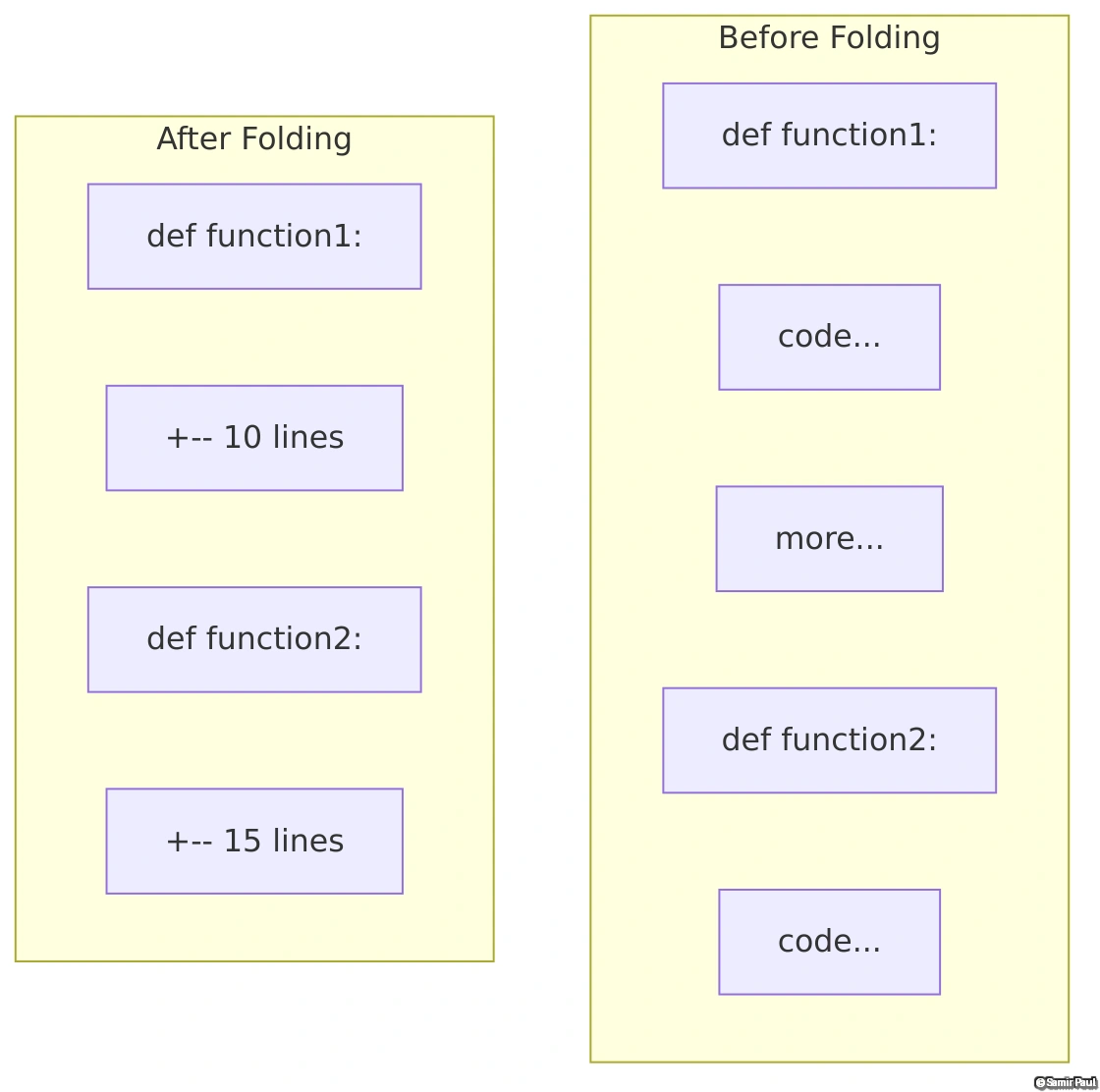
Pro Tip: Use zM to close all folds and zR to open all folds for quick file overview!
Window Splits and Layouts
Multi-Window Editing
Edit multiple files simultaneously or view different parts of the same file. Essential for comparing code, referencing documentation while coding, or split-screen workflows.
Window Split Commands
" Creating splits
:split [file] = Horizontal split (Ctrl-W s)
:vsplit [file] = Vertical split (Ctrl-W v)
:new = New horizontal split with empty buffer
:vnew = New vertical split with empty buffer
" Navigating between windows
CTRL-W h = Move to window on left
CTRL-W j = Move to window below
CTRL-W k = Move to window above
CTRL-W l = Move to window on right
CTRL-W w = Cycle through windows
CTRL-W p = Go to previous window
" Resizing windows
CTRL-W = = Make all windows equal size
CTRL-W _ = Maximize current window height
CTRL-W | = Maximize current window width
CTRL-W + = Increase height
CTRL-W - = Decrease height
CTRL-W > = Increase width
CTRL-W < = Decrease width
:resize 20 = Set window height to 20 lines
:vertical resize 80 = Set window width to 80 columns
" Moving windows
CTRL-W H = Move window to far left
CTRL-W J = Move window to bottom
CTRL-W K = Move window to top
CTRL-W L = Move window to far right
CTRL-W r = Rotate windows
CTRL-W x = Exchange with next window
" Closing windows
CTRL-W q = Quit window (close)
CTRL-W c = Close window (same as :close)
CTRL-W o = Close all other windows (only keep current)
:only = Close all windows except currentWindow Layout Visualization
Different layouts for different workflows. Mix horizontal and vertical splits as needed:
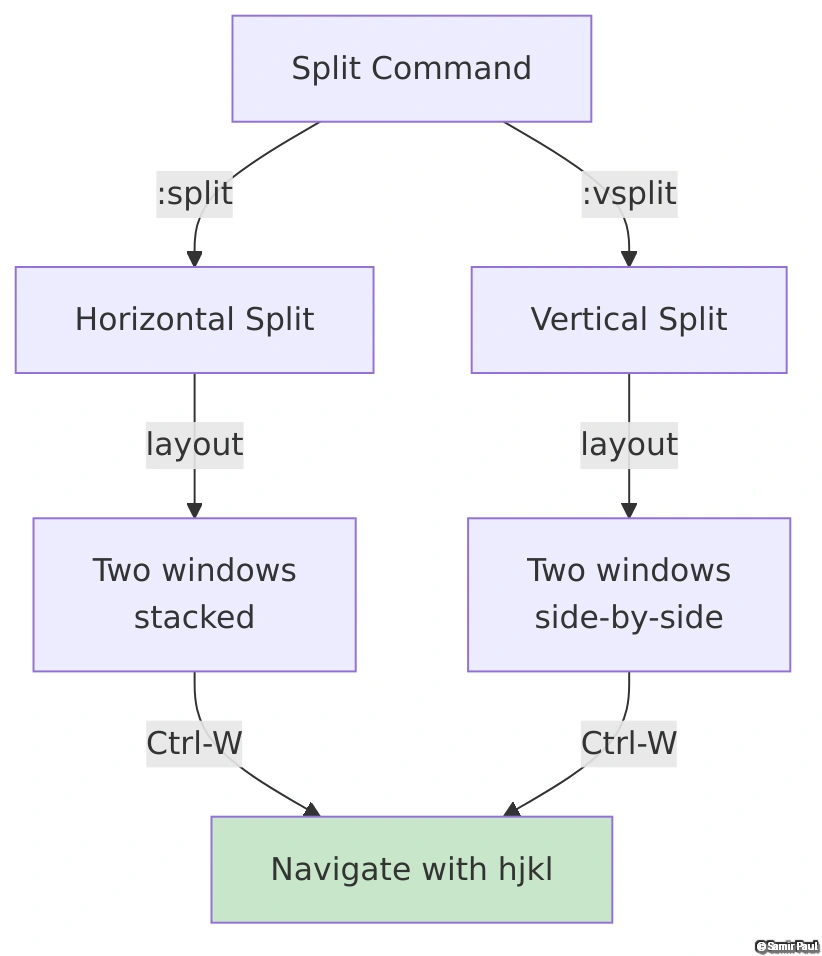
Quick Tips:
- Horizontal split:
:splitorCTRL-W s - Vertical split:
:vsplitorCTRL-W v - Navigate: Use
CTRL-W+ direction keys (hjkl)
Practical Split Workflow
" Open file in horizontal split, reference while coding
:split reference.md
" Open related files side-by-side
:vsplit related_code.py
" Quick split for viewing same file in two places
CTRL-W v " Vertical split same file
50G " Go to line 50 in one split
CTRL-W w " Switch to other split
100G " Go to line 100
" Now you can see lines 50 and 100 simultaneously!
" Comparing two files
:split file1.txt
:vsplit file2.txt
" Side-by-side comparisonBuffers, Windows, and Tabs Explained
Understanding Vim’s Three-Layer System
This is often confusing for beginners. Vim has three concepts:
- Buffer: A file in memory
- Window: A view into a buffer
- Tab: A collection of windows
Buffers vs Windows vs Tabs
Understanding the relationship between these three concepts is crucial:
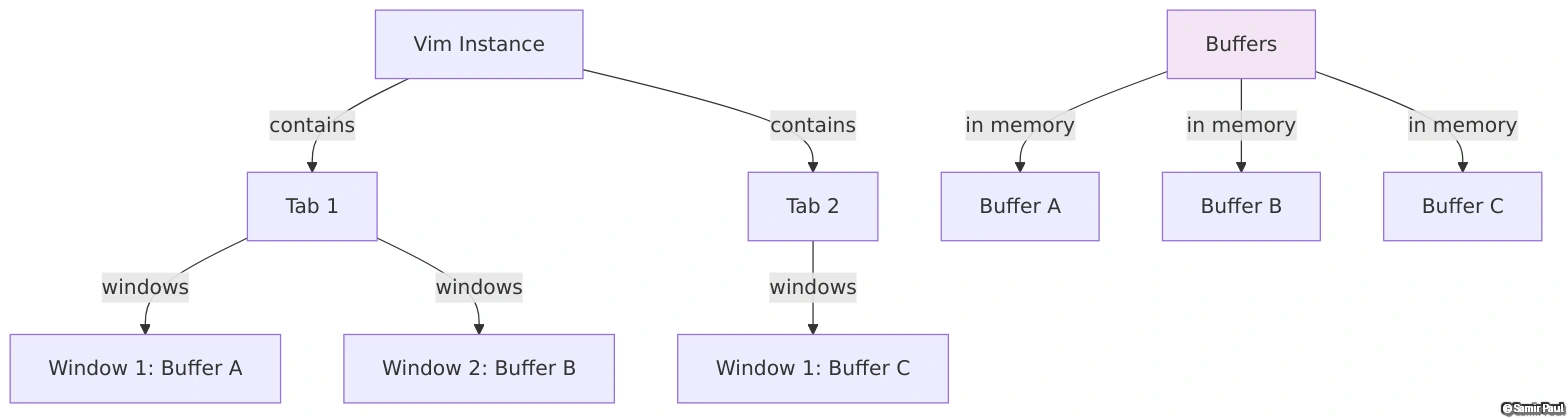
Key Insight: One buffer can be displayed in multiple windows simultaneously, and buffers remain in memory even when not visible!
Buffer Management
" Opening buffers
:e file.txt = Edit (open) file in current buffer
:badd file.txt = Add file to buffer list (don't show)
:buffer N = Switch to buffer number N
:buffer file = Switch to buffer by name
" Navigating buffers
:ls = List all buffers (shows numbers and status)
:bnext = Next buffer (also :bn)
:bprevious = Previous buffer (also :bp)
:bfirst = First buffer
:blast = Last buffer
:b# = Switch to alternate buffer (last viewed)
" Buffer info in :ls output
" %a = Active buffer (visible in current window)
" # = Alternate buffer (last viewed)
" + = Modified buffer
" - = Unmodifiable buffer
" = = Readonly buffer
" h = Hidden buffer
" Closing buffers
:bd = Delete (close) current buffer
:bd 3 = Delete buffer 3
:bd file.txt = Delete buffer by name
:%bd = Delete all buffers
:bufdo bd = Delete all buffers (iterate through)
" Working with multiple buffers
:args file1 file2 file3 = Set argument list
:argdo %s/old/new/g = Execute command on all args
:bufdo update = Save all modified buffersTab Management
" Creating tabs
:tabnew = New empty tab
:tabedit file = Open file in new tab
:tabfind file = Find and open file in new tab
" Navigating tabs
gt = Next tab (also :tabnext)
gT = Previous tab (also :tabprevious)
3gt = Go to tab 3
:tabfirst = Go to first tab
:tablast = Go to last tab
" Moving tabs
:tabmove 0 = Move current tab to first position
:tabmove = Move current tab to last position
:tabmove +1 = Move tab one position right
:tabmove -1 = Move tab one position left
" Closing tabs
:tabclose = Close current tab
:tabonly = Close all other tabsAdvanced Search Techniques
Quick Search Commands
* = Search forward for word under cursor
# = Search backward for word under cursor
g* = Search forward for partial word match
g# = Search backward for partial word match
gd = Go to local declaration
gD = Go to global declaration
gf = Go to file under cursor (open file)
CTRL-] = Jump to tag (requires ctags)
CTRL-T = Jump back from tag
" Searching in multiple files
:vimgrep /pattern/ **/*.py = Search in all Python files recursively
:grep pattern **/*.py = Use external grep
:cn = Next match
:cp = Previous match
:copen = Open quickfix window with results
:cclose = Close quickfix windowSearch Across Multiple Files
" Using vimgrep (built-in)
:vimgrep /TODO/ **/*.js " Search all JS files
:copen " Open quickfix with results
:cn " Jump to next match
:cp " Jump to previous match
" Using external grep (faster)
:grep -r "function" . " Recursive grep
:copen " View results
" Search in open buffers only
:bufdo vimgrepadd /pattern/ %
" Location list (per-window quickfix)
:lvimgrep /pattern/ **/*.py " Search, use location list
:lopen " Open location list
:lnext " Next in location listAutocomplete and Omnicomplete
Built-in Autocomplete
Vim has powerful autocomplete without plugins! Use CTRL-N and CTRL-P for basic completion, or CTRL-X submodes for advanced completion.
Autocomplete Commands
" In Insert Mode:
CTRL-N = Next completion (searches forward in file)
CTRL-P = Previous completion (searches backward)
" CTRL-X submodes (press in insert mode)
CTRL-X CTRL-N = Complete from current buffer
CTRL-X CTRL-F = Complete filenames
CTRL-X CTRL-L = Complete whole lines
CTRL-X CTRL-K = Complete from dictionary
CTRL-X CTRL-T = Complete from thesaurus
CTRL-X CTRL-I = Complete from current and included files
CTRL-X CTRL-] = Complete tags
CTRL-X CTRL-O = Omnicomplete (language-specific)
" Navigate completion menu
CTRL-N = Select next item
CTRL-P = Select previous item
CTRL-Y = Accept selection
CTRL-E = Cancel completionAutocomplete Configuration
" Basic autocomplete settings
set completeopt=longest,menuone " Better completion menu
set complete+=kspell " Spell checking suggestions
" Enable omnicomplete for programming
filetype plugin on
set omnifunc=syntaxcomplete#Complete
" Auto-trigger completion after certain chars
autocmd FileType python set omnifunc=pythoncomplete#Complete
autocmd FileType javascript set omnifunc=javascriptcomplete#CompleteJS
autocmd FileType html set omnifunc=htmlcomplete#CompleteTags
autocmd FileType css set omnifunc=csscomplete#CompleteCSS
" Dictionary completion
set dictionary=/usr/share/dict/wordsSessions: Save Your Workspace
Sessions Save Your Entire Vim State
Save your open files, window layouts, tabs, and even command history. Perfect for project-based workflows.
Session Commands
" Creating sessions
:mksession ~/my-project.vim " Create session file
:mks ~/my-project.vim " Shorthand
" Session includes:
" - All open buffers
" - Window layouts and splits
" - Tab pages
" - Current directory
" - Vim options and mappings
" - Marks and registers (optional)
" Loading sessions
vim -S ~/my-project.vim " Load session on startup
:source ~/my-project.vim " Load session from Vim
" Updating existing session
:mks! " Overwrite current session
" Session options
set sessionoptions=blank,buffers,curdir,folds,help,tabpages,winsize
" Auto-save session on exit (add to .vimrc)
autocmd VimLeave * mksession! ~/.vim/session/last.vimPractical Session Workflow
" Setup for a project
cd ~/projects/myapp
vim .
" Open relevant files
:e src/main.py
:vsplit src/utils.py
:split tests/test_main.py
" Arrange windows as needed
CTRL-W = (equalize sizes)
" Save this layout as session
:mks! ~/vim-sessions/myapp.vim
" Next day: restore entire workspace
vim -S ~/vim-sessions/myapp.vim
" Everything back as it was:
" - Same files open
" - Same window layout
" - Same working directoryDiff Mode: Compare Files
Diff Commands
" Start diff mode
vimdiff file1.txt file2.txt " From command line
:vertical diffsplit file2.txt " From within Vim
" Diff navigation
]c = Jump to next change
[c = Jump to previous change
" Diff operations
do = Obtain (get) changes from other file
dp = Put changes to other file
:diffget = Same as 'do' (obtain)
:diffput = Same as 'dp' (put)
" Diff options
:diffupdate = Recalculate diff (if changes occurred)
:diffoff = Turn off diff mode
:set diffopt=filler,vertical " Configuration
" Resolve merge conflicts
:set diffopt+=iwhite " Ignore whitespace
:diffget LOCAL " Get changes from LOCAL
:diffget REMOTE " Get changes from REMOTEDiff Visualization
Diff Mode Display:
┌──────────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────────┐
│ file1.txt │ file2.txt │
├──────────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────────┤
│ line 1: same │ line 1: same │
│ line 2: different │ line 2: CHANGED │
│ └─ highlighted red │ └─ highlighted green │
│ line 3: same │ line 3: same │
│ line 4: only in file1 │ ───────────────────── │
│ └─ shown with "+" │ (missing in file2) │
│ line 5: same │ line 4: same │
└──────────────────────────────┴──────────────────────────────┘
Navigation:
]c → Jump to next difference
[c → Jump to previous difference
do → Obtain change from other window
dp → Put change to other windowSpell Checking
Spell Check Commands
" Enable/disable spell checking
:set spell " Turn on spell check
:set nospell " Turn off spell check
:set spelllang=en_us " Set language to US English
:set spelllang=en_gb " Set language to British English
" Navigate spelling errors
]s = Next misspelled word
[s = Previous misspelled word
]S = Next misspelled word (skip rare words)
[S = Previous misspelled word (skip rare words)
" Fix spelling errors
z= = Suggest corrections (shows menu)
1z= = Use first suggestion automatically
zg = Add word to dictionary (good word)
zw = Mark word as misspelled (wrong word)
zug = Undo zg (remove from dictionary)
zuw = Undo zw
" Custom dictionary
:set spellfile=~/.vim/spell/custom.utf-8.addAdvanced Text Transformations
Case Transformations
~ = Toggle case of character under cursor
g~{motion} = Toggle case of motion
gu{motion} = Lowercase motion
gU{motion} = Uppercase motion
" Examples
gUiw = Uppercase inner word
guap = Lowercase paragraph
g~~ = Toggle case of current line
gUU = Uppercase current line
guu = Lowercase current line
" In visual mode
V = Select line
U = Uppercase selection
u = Lowercase selection
~ = Toggle caseText Joining and Splitting
J = Join current line with next (removes newline)
5J = Join next 5 lines
gJ = Join without adding space
" Example:
" Before:
" line1
" line2
" line3
" After pressing J:
" line1 line2
" line3
" After pressing gJ (no space):
" line1line2Sorting and Filtering
" Sort lines
:sort = Sort lines alphabetically
:sort! = Sort in reverse
:sort n = Sort numerically
:sort u = Sort and remove duplicates
" Sort range
:10,20sort = Sort lines 10-20
:'<,'>sort = Sort visual selection
" Filter through external command
:%!sort = Filter entire file through Unix sort
:%!uniq = Remove duplicate lines
:10,20!sort = Sort lines 10-20 with Unix sort
" Example: Format JSON
:%!python -m json.tool " Pretty-print JSON fileIncrement and Decrement Numbers
CTRL-A = Increment number under cursor
CTRL-X = Decrement number under cursor
10CTRL-A = Increment by 10
" Visual block increment (create sequences)
CTRL-V = Block select numbers
g CTRL-A = Increment sequentially (1,2,3,4...)
g CTRL-X = Decrement sequentially
" Example: Create numbered list
1 = Start with 1
CTRL-V = Block select vertically
5j = Select 5 lines
g CTRL-A = Now you have: 1,2,3,4,5,6Quickfix and Location Lists
Quickfix: Central Error/Search Results
Quickfix list is a special window showing errors, search results, or any list of file locations. Essential for compilation errors, search results, and linting.
Quickfix Commands
" Opening quickfix
:copen = Open quickfix window
:cclose = Close quickfix window
:cwindow = Open only if there are errors
" Navigation
:cnext = Next item (also :cn)
:cprevious = Previous item (also :cp)
:cfirst = First item
:clast = Last item
:cc N = Jump to item N
" Loading errors/results
:cfile file = Load errors from file
:cgetfile file = Load errors (don't jump)
:cexpr expr = Set quickfix from expression
" Quickfix for compilation
:make = Run make, populate quickfix with errors
:set makeprg=gcc\ % " Set compiler commandLocation List Commands
" Location list (per-window version of quickfix)
:lopen = Open location list
:lclose = Close location list
:lnext = Next item (ln)
:lprevious = Previous item (lp)
:lfirst = First item
:llast = Last item
" Location list is specific to each window
" Quickfix is global to all windowsQuickfix Workflow Example
" 1. Search for TODO comments across project
:vimgrep /TODO/ **/*.py
" 2. Open quickfix with results
:copen
" 3. Navigate through results
:cn " Next TODO
:cp " Previous TODO
" 4. Jump directly to item 5
:cc 5
" 5. Close quickfix
:cclose
" Quickfix window looks like:
" src/main.py|23 col 5| # TODO: Fix this bug
" src/utils.py|45 col 8| # TODO: Refactor
" tests/test.py|12 col 3| # TODO: Add testCommand History and Repeat
Command History
" In command mode (:)
<Up>/<Down> = Navigate command history
:history = Show command history
:history / = Show search history
q: = Open command history window (editable!)
q/ = Open search history window
CTRL-F = Open command history from command line
" In history window:
<Enter> = Execute command under cursor
:q = Close history windowRepeat Commands
. = Repeat last change
@: = Repeat last command-line command
@@ = Repeat last @x macro
" Practical examples
dd = Delete line
. = Delete another line (repeats dd)
:s/old/new/ = Substitute on one line
@: = Repeat substitution on current line
" Repeat with count
3. = Repeat last change 3 times
5@: = Repeat last command 5 timesAdvanced Vim Tricks
Multiple Cursors Simulation
" Insert at multiple positions
CTRL-V = Block visual mode
5j = Select 5 lines
I = Insert at beginning of all lines
text<ESC> = Type text, press ESC
→ text appears on all selected lines!
" Append at multiple positions
CTRL-V = Block select
5j = Select lines
$ = Go to end of lines
A = Append at end
text<ESC> = Text appended to all lines
" Change multiple lines
CTRL-V = Block select
5j = Select lines
c = Change
new_text<ESC> = Replaced on all linesGlobal Command Magic
" Syntax: :g/pattern/command
" Delete all lines containing pattern
:g/TODO/d = Delete all lines with TODO
" Delete all lines NOT containing pattern
:g!/pattern/d = Keep only lines with pattern
:v/pattern/d = Same as above
" Execute command on matching lines
:g/function/normal @a = Run macro 'a' on lines with 'function'
:g/import/m$ = Move all import lines to end
" Copy matching lines
:g/error/t$ = Copy all lines with 'error' to end
" Multiple commands
:g/pattern/d | g/other/d = Delete lines matching either patternEx Command Tricks
" Read external command output
:r!date = Insert current date
:r!ls = Insert directory listing
:0r!cat file = Insert file contents at top
" Write to command
:w !sudo tee % = Save file with sudo (when opened without sudo)
:%!xxd = Convert file to hex dump
:%!xxd -r = Convert hex back to binary
" Execute shell command and read output
:read !grep pattern file.txt
" Substitute tricks
:%s/\v(\w+)\s+(\w+)/\2 \1/g = Swap two words
:%s/\n\n/\r/g = Replace double newlines with single
:%s/\s\+$// = Remove trailing whitespaceVim Command Line Editing
" In command mode (:)
CTRL-B = Beginning of line
CTRL-E = End of line
CTRL-W = Delete word before cursor
CTRL-U = Delete to beginning
CTRL-R " = Insert contents of register
CTRL-R % = Insert current filename
CTRL-R / = Insert last search pattern
" Example
:e CTRL-R % = :e currentfile.txt (inserts current filename)Performance and Optimization
Profiling Vim Performance
" Profile startup time
vim --startuptime startup.log file.txt
" Examine startup.log to see what's slow
" Profile runtime
:profile start profile.log
:profile func *
:profile file *
" Do operations...
:profile pause
:noautocmd qall
" Check what's taking time
" View profile.logOptimization Tips
" Speed up for large files
set synmaxcol=200 " Don't syntax highlight long lines
set lazyredraw " Don't redraw during macros
set ttyfast " Fast terminal connection
set nocursorline " Disable cursor line highlight
set norelativenumber " Disable relative numbers
" Disable swap and backup for speed
set noswapfile
set nobackup
set nowritebackup
" Limit undo history
set undolevels=100
" Auto-command to disable features for large files
autocmd BufReadPre * if getfsize(bufname("%")) > 1000000 | setlocal syntax=off | endifAdvanced Configuration
Complete .vimrc Setup
" ============================================================================
" GENERAL SETTINGS
" ============================================================================
set nocompatible " Use Vim defaults, not Vi
set encoding=utf-8 " Use UTF-8 encoding
set fileencoding=utf-8
" ============================================================================
" DISPLAY
" ============================================================================
syntax on " Enable syntax highlighting
set number " Show line numbers
set relativenumber " Relative numbering (jump distance)
set cursorline " Highlight current line
set termguicolors " Enable 24-bit colors
set background=dark " Dark color scheme
colorscheme industry " Use preferred colorscheme
" ============================================================================
" INDENTATION
" ============================================================================
set tabstop=4 " Display tabs as 4 spaces
set shiftwidth=4 " Indentation size
set expandtab " Use spaces instead of tabs
set autoindent " Auto-indent new lines
set smartindent " Smart indentation
set shiftround " Round indent to shiftwidth
" ============================================================================
" SEARCH
" ============================================================================
set ignorecase " Case insensitive search
set smartcase " Except uppercase triggers case-sensitive
set incsearch " Highlight matches while typing
set hlsearch " Highlight all matches
set wrapscan " Wrap search around file
" ============================================================================
" BEHAVIOR
" ============================================================================
set backspace=indent,eol,start " Allow backspace in insert mode
set hidden " Allow unsaved buffers
set report=0 " Always report changes
set completeopt=longest,menuone " Better autocomplete
set mouse=a " Enable mouse support
set clipboard=unnamedplus " Use system clipboard
" ============================================================================
" PERFORMANCE
" ============================================================================
set lazyredraw " Don't redraw during macros
set ttyfast " Faster redraws
set synmaxcol=200 " Don't highlight very long lines
" ============================================================================
" UI ENHANCEMENTS
" ============================================================================
set statusline=%F%m%r%h%w\ [%{&ff}]\ %y\ [%p%%]\ %l:%c
set laststatus=2 " Always show status line
set showmatch " Highlight matching brackets
set showmode " Show current mode
set showcmd " Show partial command
" ============================================================================
" KEYBINDINGS - Custom mappings
" ============================================================================
let mapleader = "," " Set leader to comma
" Navigate splits easier
nnoremap <C-j> <C-w>j
nnoremap <C-k> <C-w>k
nnoremap <C-h> <C-w>h
nnoremap <C-l> <C-w>l
" Quick escape
inoremap jj <Esc>
inoremap kk <Esc>
" Clear search highlighting
nnoremap <leader>h :noh<CR>
" Quick save
nnoremap <leader>w :w<CR>
nnoremap <leader>q :q<CR>Plugin Management
Popular Plugin Managers
Plugin Ecosystem
Vim’s power comes from its plugin ecosystem. Thousands of plugins extend functionality for every workflow imaginable.
vim-plug (Recommended - Easy to use):
" Install vim-plug first:
" curl -fLo ~/.vim/autoload/plug.vim --create-dirs \
" https://raw.githubusercontent.com/junegunn/vim-plug/master/plug.vim
" In .vimrc:
call plug#begin('~/.vim/plugged')
Plug 'vim-airline/vim-airline' " Better statusline
Plug 'preservim/nerdtree' " File explorer
Plug 'junegunn/fzf.vim' " Fuzzy finder
Plug 'tpope/vim-surround' " Surround text objects
Plug 'tpope/vim-commentary' " Easy comments
Plug 'jiangmiao/auto-pairs' " Auto bracket pairing
Plug 'vim-syntastic/syntastic' " Syntax checking
Plug 'neoclide/coc.nvim' " Autocompletion
call plug#end()
" Install plugins: :PlugInstall
" Update plugins: :PlugUpdate
" Clean unused: :PlugCleanEssential Plugin Recommendations
| Plugin | Purpose | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| vim-airline | Enhanced statusline | Better visual feedback |
| nerdtree | File browser | Project file navigation |
| fzf.vim | Fuzzy finder | Fast file/buffer search |
| vim-surround | Parentheses/quotes | Easily change delimiters |
| vim-commentary | Comments | Toggle comments easily |
| coc.nvim | Autocompletion | Intelligent code completion |
| vim-fugitive | Git integration | Git operations from Vim |
| vim-repeat | Repeat plugin actions | . works with plugins |
Introduction to Vimscript
Vimscript is Quirky
Vimscript is Vim’s built-in scripting language. It’s powerful but unconventional (variables need sigils, strings behave oddly, scoping is complex). Many prefer Lua or Python for plugins, but Vimscript is essential for .vimrc customization.
Basic Vimscript
" Comments start with double quotes
" ===== VARIABLES =====
let g:myvar = 10 " Global variable
let l:myvar = 20 " Local variable
let s:myvar = 30 " Script variable
" ===== DATA TYPES =====
let string_var = "hello"
let number_var = 42
let float_var = 3.14
let list_var = [1, 2, 3, 4]
let dict_var = {'name': 'John', 'age': 30}
" ===== CONDITIONALS =====
if condition
echo "True"
elseif other_condition
echo "Also true"
else
echo "False"
endif
" ===== LOOPS =====
for item in list_var
echo item
endfor
while condition
" do something
endwhile
" ===== FUNCTIONS =====
function! MyFunction(arg1, arg2)
let result = arg1 + arg2
return result
endfunction
call MyFunction(5, 10) " Call function
" ===== OPERATORS =====
" Concatenation uses . not +
let full_str = "Hello" . " " . "World"Custom Commands and Mappings
" ===== CUSTOM COMMANDS =====
command! MyCommand echo "Custom command executed"
command! GreetMe call GreetUser("Vim User")
" ===== KEYBINDINGS =====
nnoremap <leader>t :tabnew<CR> " Normal mode
inoremap <leader>t <Esc>:tabnew<CR> " Insert mode
vnoremap <leader>y :'<,'>y+<CR> " Visual mode
" <leader> uses mapleader (usually \\ or ,)
" <CR> = Enter
" <Esc> = Escape
" <C-x> = Ctrl+x
" <S-x> = Shift+x
" Conditional mapping
if has('nvim')
nnoremap <leader>t :split<CR>
else
nnoremap <leader>t :tabnew<CR>
endif
" ===== USEFUL CONDITIONALS =====
if has('python') " Python support
if has('clipboard') " Clipboard support
if has('nvim') " Neovim specificProfessional Workflows and Tips
Multi-File Editing
" Opening multiple files
vim file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt
" Buffer commands
:ls " List all buffers
:bn " Next buffer
:bp " Previous buffer
:bd " Delete (close) buffer
:b filename " Go to buffer by name
:b3 " Go to buffer 3
" Tabs (Vim's "workspaces")
:tabnew " New tab
:tabnext / gt " Next tab
:tabprevious / gT " Previous tab
:tabclose " Close tab
" Split windows
:split file.txt " Horizontal split
:vsplit file.txt " Vertical split
<C-w>w " Switch windows
<C-w>= " Equalize window sizes
<C-w>_ " Maximize current windowWorking with Large Files
" Disable features for speed
:set noswapfile " No swap file
:set noundofile " No undo history
:set synmaxcol=80 " Limit syntax highlighting column
:syntax off " Disable syntax highlighting
" Navigate efficiently
:set nowrap " Don't wrap lines
:set lazyredraw " Lazy redraw
G " Go to end
gg " Go to start
50% " Go to 50% of file
" Use grep to find in large files
:grep pattern filename
" Stream editing
:read !cat largefile | head -100 " Read first 100 lines onlyGit Integration
" Using vim-fugitive plugin:
:Git status " Show git status
:Git add % " Stage current file
:Git commit " Commit changes
:Git push " Push changes
:Git diff " Show diff
:Git log " Show commit log
:Gblame " Show blame (who edited each line)
" Viewing diffs
:Gvdiffsplit " Show diff in vertical split
]c / [c " Navigate changesCommon Issues and Solutions
Frequent Problems
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Stuck in Insert Mode | Press ESC or CTRL-C to return to Normal Mode |
| Can’t exit Vim | Type :q (quit) or :q! (quit without saving) |
| Accidentally entered Command Mode | Press ESC to go back to Normal Mode |
| Keys not responding as expected | Make sure you’re in Normal Mode, not Insert Mode |
| Search highlighting won’t clear | Run :noh or :nohlsearch |
| Want to undo multiple changes | Press u multiple times or 20u for 20 undos |
Performance Issues
" Diagnose startup time
vim --startuptime startup.log
" Disable unneeded features
:set nocompatible
:set lazyredraw
:set ttyfast
" Limit syntax highlighting for huge files
autocmd BufReadPre * if getfsize(bufname('%')) > 10000000 | syntax off | endif
" Reduce number of active plugins
" Keep only plugins you actually useRecommended Learning Path
Phase 1: Fundamentals (Week 1-2)
Master These First
Don’t move to advanced techniques until these are muscle memory. Spend 15-30 minutes daily practicing.
Essential Skills:
- Mode transitions (ESC, i, v, :)
- Basic motions (hjkl, w, b, $, ^)
- Operators (d, c, y)
- Save and quit (:w, :q, :wq)
Practice:
# Interactive Vim tutorial (built-in)
vimtutor
# Practice daily for 2 weeks
# Open a file and practice moving, editing, savingPhase 2: Intermediate (Week 3-4)
Skills:
- Text objects (iw, i", i{, ap)
- Visual mode (v, V, CTRL-V)
- Search and replace (/, :%s/old/new/g)
- Registers (named, special)
- Macros (qa…q, @a)
Phase 3: Advanced (Week 5+)
Skills:
- Plugin ecosystem
- Custom configuration
- Vimscript basics
- Advanced workflows
- Performance optimization
Resources for Continued Learning
Official and Quality Resources
- Built-in Help:
:helpor:help topic(comprehensive!) - Vim Manual: http://vimdoc.sourceforge.net/
- Interactive Tutor:
vimtutorcommand - Learn Vim the Smart Way: Excellent free online guide
- Practical Vim by Drew Neil: Best book on Vim
- Daily Vim Tips: Twitter account @vimtips
Community and Tools
- r/vim on Reddit: Active community
- Stack Overflow: Tag: vim
- GitHub: Thousands of plugins and configs
- VimAwesome: Plugin directory
Conclusion: Your Vim Journey Begins
Vim has a steep learning curve, but the investment pays dividends. Once mastered, you’ll edit text faster and more efficiently than ever before. Remember:
Key Takeaways
- Modes are your friend: Normal mode for navigation, Insert mode for typing
- Grammar is power: Learn operators and motions, then combine them
- Text objects are essential: They make editing feel smart and intuitive
- Practice daily: Vim skills compound over time
- Customize gradually: Start simple, add plugins and config as needed
- Join the community: Vim users love sharing tips and tricks
Start with the basics, practice consistently, and gradually explore advanced features. Within a few weeks, you’ll wonder how you ever edited without Vim.
Happy editing! 🖤
Complete Vim Workflow Diagrams
Editing Workflow Progression
VIM EDITING WORKFLOW — From Simple to Complex:
════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
LEVEL 1: Basic Editing (First Week)
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. vim file.txt → Open file │
│ 2. i → Enter insert mode │
│ 3. Type text... → Add content │
│ 4. ESC → Back to normal mode │
│ 5. :wq → Save and quit │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
LEVEL 2: Motion-Based Editing (Week 2-3)
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. vim file.txt → Open file │
│ 2. /function → Search for "function" │
│ 3. n → Next match │
│ 4. ciw → Change inner word │
│ 5. newname → Type replacement │
│ 6. ESC → Back to normal │
│ 7. n → Next occurrence │
│ 8. . → Repeat change (ciw) │
│ 9. :wq → Save and quit │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
LEVEL 3: Advanced Multi-File Workflow (Week 4+)
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. vim -p file1 file2 → Open in tabs │
│ 2. :vimgrep /TODO/ ** → Search all files │
│ 3. :copen → View results │
│ 4. :cn → Next result │
│ 5. ciw → Change word │
│ 6. qa → Start recording macro │
│ 7. ...edits... → Make changes │
│ 8. q → Stop recording │
│ 9. @a → Replay on next item │
│ 10. :bufdo update → Save all buffers │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Problem-Solving Decision Tree
WHICH VIM FEATURE TO USE?
══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
Need to edit text?
│
├─ Single change?
│ ├─ YES → Use operators (d, c, y) + motions (w, $, })
│ └─ NO → Continue below
│
├─ Repetitive task?
│ ├─ Same change many times → Record macro (qa...q, @a)
│ ├─ Pattern-based → Use :g/pattern/command
│ └─ Multiple files → :bufdo or :argdo
│
├─ Finding code?
│ ├─ In current file → Use / search, *, #
│ ├─ Multiple files → :vimgrep or :grep
│ ├─ Jump to definition → gd or CTRL-]
│ └─ Recent locations → CTRL-O / CTRL-I
│
├─ Navigating?
│ ├─ Within file → Marks (ma, `a)
│ ├─ Between files → Buffers (:bn, :bp)
│ ├─ Multiple layouts → Windows (CTRL-W s/v)
│ └─ Different projects → Tabs (gt, gT)
│
└─ Large-scale refactor?
├─ Complex → Record macro + :g command
├─ Multiple files → :bufdo with macro
└─ Precise pattern → Regex substitutionReal-World Refactoring Example
SCENARIO: Rename variable 'oldVar' to 'newVar' across project
══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
METHOD 1: Manual (Small Project)
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. /oldVar<Enter> Search for oldVar │
│ 2. * Highlight all occurrences │
│ 3. ciw Change inner word │
│ 4. newVar<ESC> Type new name │
│ 5. n Next occurrence │
│ 6. . Repeat change │
│ 7. Repeat steps 5-6... │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
METHOD 2: Macro (Medium Project)
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. /oldVar<Enter> Search first occurrence │
│ 2. qa Start recording to register a │
│ 3. ciwn ewVar<ESC> Change word │
│ 4. n Next occurrence │
│ 5. q Stop recording │
│ 6. 100@a Replay 100 times (safe) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
METHOD 3: Substitution (Large Project)
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. :args **/*.js Add all JS files to arglist │
│ 2. :argdo %s/\<oldVar\>/newVar/gc │
│ Substitute with confirmation │
│ 3. :argdo update Save all changed files │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
METHOD 4: Advanced (Huge Project)
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. :vimgrep /\<oldVar\>/ **/*.js │
│ Find all occurrences │
│ 2. :copen Open quickfix with results │
│ 3. :cfdo %s/\<oldVar\>/newVar/g │
│ Substitute in all files │
│ 4. :cfdo update Save all changed files │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Text Object Combination Matrix
TEXT OBJECT POWER COMBINATIONS
═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
OPERATOR × TEXT OBJECT = POWERFUL COMMANDS
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
│ iw │ aw │ i" │ i( │ i{ │ ap │
─────────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┤
d │ diw │ daw │ di" │ di( │ di{ │ dap │
│ delete│delete │delete │delete │delete │delete │
│ word │ word+ │inside │inside │inside │para │
─────────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┤
c │ ciw │ caw │ ci" │ ci( │ ci{ │ cap │
│change │change │change │change │change │change │
│ word │ word+ │quote │parens │braces │para │
─────────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┤
y │ yiw │ yaw │ yi" │ yi( │ yi{ │ yap │
│ yank │ yank │ yank │ yank │ yank │ yank │
│ word │ word+ │quote │parens │braces │para │
─────────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┤
v │ viw │ vaw │ vi" │ vi( │ vi{ │ vap │
│select │select │select │select │select │select │
│ word │ word+ │quote │parens │braces │para │
─────────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼───────┤
gU │ gUiw │ gUaw │ gUi" │ gUi( │ gUi{ │ gUap │
│UPPER │UPPER │UPPER │UPPER │UPPER │UPPER │
│ word │ word+ │quote │parens │braces │para │
─────────┴───────┴───────┴───────┴───────┴───────┴───────┘
Most useful combinations:
• ciw - Change inner word (rename variable)
• di" - Delete inside quotes (remove string content)
• ci( - Change inside parentheses (edit function args)
• dap - Delete paragraph (remove code block)
• yap - Yank paragraph (copy function/block)Quick Reference Card
╔══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ VIM COMPLETE QUICK REFERENCE ║
╚══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝
┌─ MODES ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ESC Return to Normal mode (from any mode) │
│ i/I Insert before cursor / at line start │
│ a/A Append after cursor / at line end │
│ o/O Open line below / above │
│ v/V/Ctrl-V Visual: character / line / block │
│ : Command mode (Ex commands) │
│ R Replace mode (overwrite) │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ MOVEMENT ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ h/j/k/l Left / Down / Up / Right │
│ w/W Next word / WORD │
│ b/B Previous word / WORD │
│ e/E End of word / WORD │
│ 0/^/$ Start of line / First non-blank / End │
│ gg/G Start / end of file │
│ {/} Previous / next paragraph │
│ % Jump to matching bracket │
│ fx/Fx Find char 'x' forward / backward │
│ */# Search word under cursor forward / backward │
│ Ctrl-O/Ctrl-I Jump to older / newer position │
│ ma / `a Set mark 'a' / Jump to mark 'a' │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ EDITING ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ x/X Delete char at / before cursor │
│ dd Delete line │
│ D Delete to end of line │
│ d{motion} Delete motion (dw, d$, dip, di") │
│ c{motion} Change motion (delete + insert mode) │
│ y{motion} Yank (copy) motion (yy = yank line) │
│ p/P Paste after / before cursor │
│ u/Ctrl-R Undo / Redo │
│ . Repeat last change │
│ J Join lines │
│ ~ Toggle case │
│ gU/gu{motion} Uppercase / lowercase motion │
│ Ctrl-A/Ctrl-X Increment / decrement number │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ TEXT OBJECTS (use with operators: d, c, y, v, gU, etc.) ─────────────┐
│ iw/aw Inner word / a word (with space) │
│ i"/a" Inside / around double quotes │
│ i'/a' Inside / around single quotes │
│ i(/a( or ib/ab Inside / around parentheses │
│ i{/a{ or iB/aB Inside / around braces │
│ i[/a[ Inside / around brackets │
│ it/at Inside / around HTML/XML tag │
│ ip/ap Inner / a paragraph │
│ is/as Inner / a sentence │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ SEARCH & REPLACE ────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ /pattern Search forward │
│ ?pattern Search backward │
│ n/N Next / previous match │
│ */# Search word under cursor forward / backward │
│ :noh Clear search highlighting │
│ :s/old/new/ Replace first on line │
│ :s/old/new/g Replace all on line │
│ :%s/old/new/g Replace all in file │
│ :%s/old/new/gc Replace all with confirmation │
│ :10,20s/old/new/g Replace in lines 10-20 │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ FILES & BUFFERS ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ :w Save file │
│ :w filename Save as filename │
│ :q Quit (fails if unsaved) │
│ :q! Quit without saving │
│ :wq or :x Save and quit │
│ :e filename Open file │
│ :ls List buffers │
│ :bn/:bp Next / previous buffer │
│ :bd Delete (close) buffer │
│ :b3 Switch to buffer 3 │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ WINDOWS & TABS ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ :split/:sp Horizontal split │
│ :vsplit/:vsp Vertical split │
│ Ctrl-W s/v Split horizontal / vertical │
│ Ctrl-W h/j/k/l Navigate to window left/down/up/right │
│ Ctrl-W w Cycle windows │
│ Ctrl-W q Close window │
│ Ctrl-W = Equalize window sizes │
│ :tabnew New tab │
│ gt/gT Next / previous tab │
│ :tabclose Close tab │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ VISUAL MODE ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ v Character-wise visual │
│ V Line-wise visual │
│ Ctrl-V Block visual (rectangular selection) │
│ o Jump to other end of selection │
│ >/<< Indent right / left │
│ d/c/y Delete / change / yank selection │
│ u/U Lowercase / uppercase │
│ = Auto-indent │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ MACROS ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ qa Start recording macro in register 'a' │
│ q Stop recording │
│ @a Play macro from register 'a' │
│ @@ Repeat last macro │
│ 10@a Execute macro 10 times │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ REGISTERS ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ "ayy Yank line to register 'a' │
│ "ap Paste from register 'a' │
│ "0 Last yank │
│ "1-"9 Last 9 deletions │
│ "+ System clipboard │
│ :reg Show all registers │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ MARKS & JUMPS ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ma Set mark 'a' at cursor │
│ `a Jump to exact position of mark 'a' │
│ 'a Jump to line of mark 'a' │
│ `` Jump to position before last jump │
│ `. Jump to last change │
│ Ctrl-O/Ctrl-I Navigate jump history older / newer │
│ :marks Show all marks │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ FOLDING ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ zo/zc Open / close fold │
│ za Toggle fold │
│ zM/zR Close all / open all folds │
│ zf{motion} Create fold │
│ zd Delete fold │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ ADVANCED COMMANDS ───────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ :g/pattern/d Delete all lines matching pattern │
│ :v/pattern/d Delete lines NOT matching pattern │
│ :sort Sort lines │
│ :! command Execute external command │
│ :%!sort Filter file through external command │
│ :r!date Insert output of command │
│ :w !sudo tee % Save with sudo │
│ gd/gD Go to local / global declaration │
│ Ctrl-N/Ctrl-P Autocomplete next / previous │
│ Ctrl-X Ctrl-F Filename completion │
│ vimdiff f1 f2 Diff two files │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ QUICKFIX ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ :vimgrep /pat/ ** Search all files │
│ :copen Open quickfix window │
│ :cn/:cp Next / previous error │
│ :cclose Close quickfix │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─ HELP & EXIT ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ :help topic Get help on topic │
│ :q Quit help window │
│ vimtutor Interactive Vim tutorial (run from shell) │
│ :qa! Quit all windows without saving (emergency exit!) │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
╔═════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ REMEMBER: Vim is a language. Learn operators, motions, and combine! ║
║ Formula: OPERATOR + [COUNT] + MOTION/TEXT-OBJECT ║
║ Example: d3w (delete 3 words), ciw (change inner word), yap (yank par) ║
╚═════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝